Haz
Edge Member-
Posts
1,458 -
Joined
-
Last visited
-
Days Won
391
Haz's Achievements
-
Haz started following 2019 diesel edge a wetbelt?
-
@sounduser: Your question may be addressed by the U.K. edition Workshop Manual sections attached below as PDF documents... Please note that I selected 177kW/240PS EcoBlue information -- if you require the lower output EcoBlue information, just let me know and I will provide it. Good luck! Engine - System Operation and Component Description - 2.0L EcoBlue Diesel - 2015-2022 Edge, Edge Vignale, Endura Workshop Manual.pdf Engine Component Location - Description and Operation - 2.0L EcoBlue Diesel - 2015-2022 Edge, Edge Vignale, Endura Workshop Manual.pdf Timing Belt - Removal and Installation - 2.0L EcoBlue Diesel - 2015-2022 Edge, Edge Vignale, Endura Workshop Manual.pdf Timing Belt Cover - Removal and Installation - 2.0L EcoBlue Diesel - 2015-2022 Edge, Edge Vignale, Endura Workshop Manual.pdf
-
Welcome to the Forum @Todd Turner! Your described repair efforts indicate this question may be unnecessary, but since you don't mention performing a Programmable Module Installation (PMI) procedure: When the ABS Module was replaced, did you configure the new ABS Module using the As-Built values contained in the ABS Module you removed? Also, when the brake lock-up symptom occurs, are you hearing the ABS pump activating? Relevant sections from the 2013 Edge Workshop Manual and Wiring Resource are attached below as PDF documents... Good Luck! Brake Pedal and Bracket - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf BRAKE PEDAL POSITION (BPP) SWITCH - Connector C2064 Pinout Diagram - 2013 Edge.pdf BRAKE PEDAL POSITION (BPP) SWITCH - Connector C2064 Location - 2013 Edge.pdf BRAKE PEDAL POSITION (BPP) SWITCH - Power Distribution Wiring Diagram - 2013 Edge.pdf Stoplamp Switch - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Component Tests - Brke System Diagnosis and Testing - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU) - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Pinpoint Test C - DTCs C0044.28, C0044.49 and C0044.64 - Diagnosis and Testing - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Wheel Speed Sensor — Front - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf
-
Historical references attached below as PDF documents... Good luck! Customer Satisfaction Program 19N09 - Left Front Door Latch Extended Coverage - 12-12-2019 - Dealer Bulletin.pdf Customer Satisfaction Program 19N09 - Left Front Door Latch Extended Coverage - 12-12-2019 - Technical Instructions.pdf TSB 18-2013 - Door Ajar Lamp Remains Illuminated When Doors Closed.pdf
-
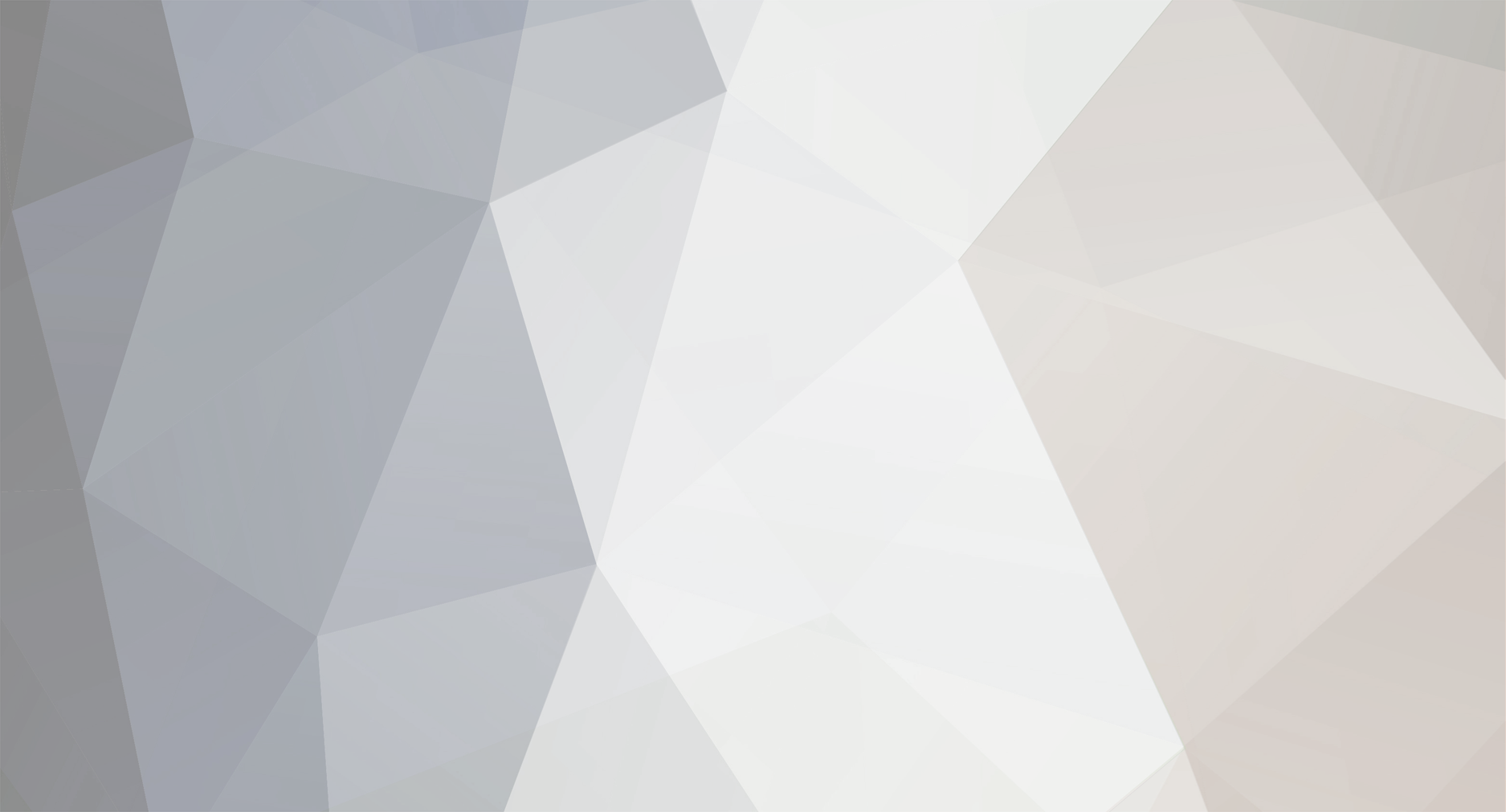
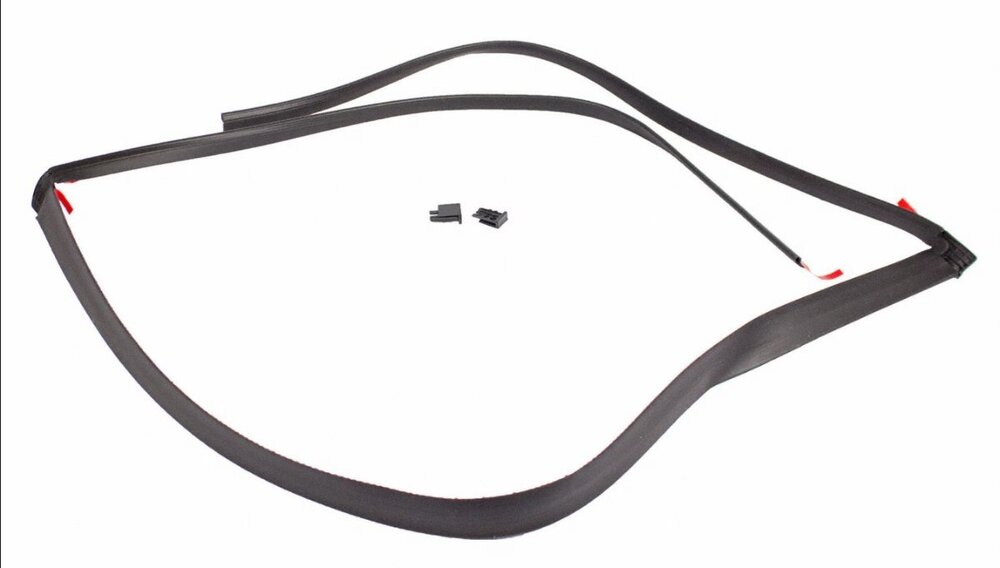
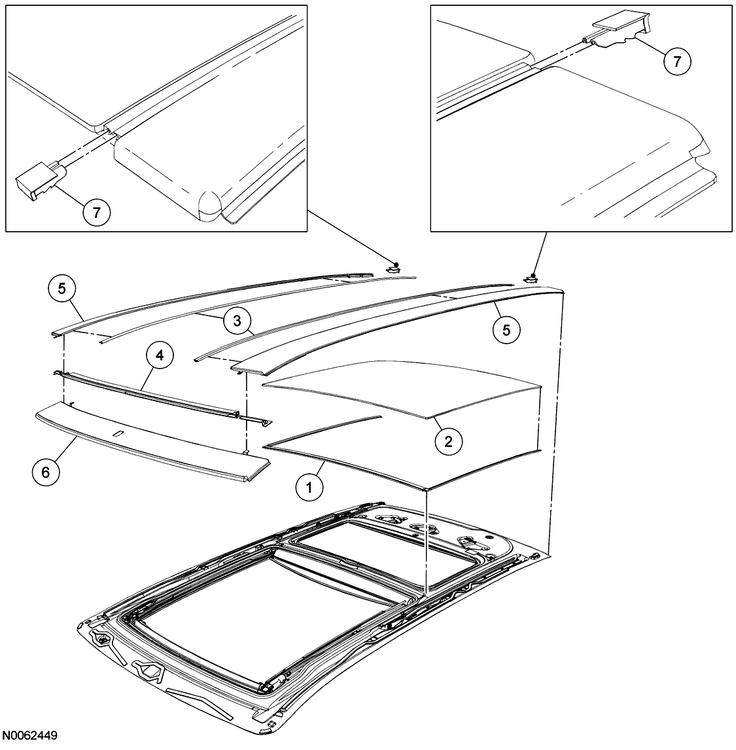
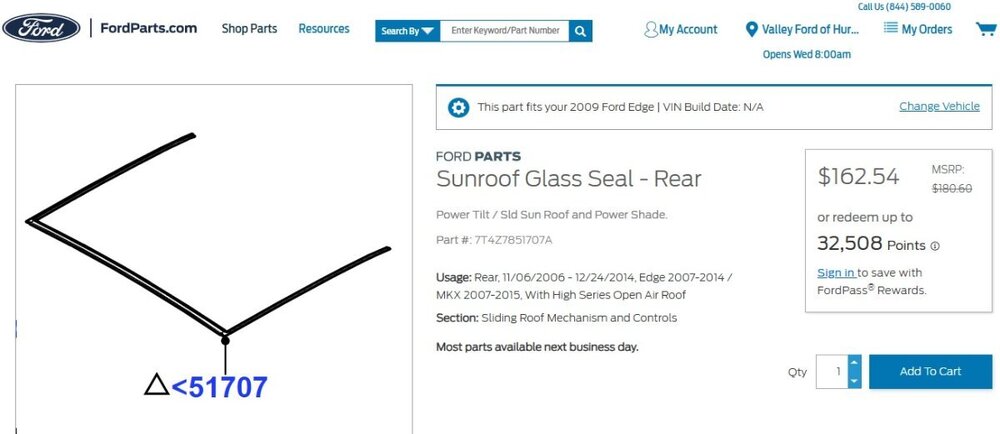
@edgemaster: The 2009 Edge Workshop Manual provides the following illustration showing the Fixed Glass panel of your Edge's Panoramic Roof. You are describing the U-shaped Fixed Glass Front Seal (item 1), which along with the two Side Trim Seals (item 3) fill the gaps at the front and on the left & right sides of the Fixed Glass panel, where channels exist to drain water to the rear of the roof, where it flows out through the left & right side End Caps (item 7)... As you may already know, the waterproof sealing of the Fixed Glass panel is provided by a continual bead of urethane adhesive applied to the metal roof structure in the shape of Path 1 or Path 2, depending upon the model year of the Edge/MKX... Ford's parts-selling website offers photos of the Front seal which may be helpful, and which appears to show the red pull-off strip for double-sided tape used to affix the Front seal to the roof, underneath the outer edges of the Fixed Glass panel... Link to this FordParts webpage The Workshop Manual does not provide any procedure relating to removal and installation of the Front seal. If it did, I expect because of the minimal clearance between the Front seal's left-hand & right-hand side legs and the seals on the Side Trim pieces, the procedure might involve removal of the Fixed Glass panel by cutting the bead of urethane sealant, cleaning residue from the glass panel and the metal roof, then installing of the Front seal on the roof, apply the continuous bead of urethane sealant, and install the Fixed Glass panel, all of which would very likely involve a professional glass installer. Working clearances between the rear of the Moving Glass panel and the front of the Fixed Glass panel are greater, however, so if the Front seal is only deteriorated on the front, then it might be possible to cut the existing Front seal away from its side legs, and similarly cut the replacement Front seal after clearing away all remaining rubber from underneath the front edge of the Fixed Glass panel. I would say, before attempting any of this, it would be prudent to use a feeler gage to assess how much clearance or compression-on-the-seal exists between the bottom of the glass panel and the metal rooftop. If the double-sided-taped seal cannot be freely inserted and affixed underneath the front edge of the Fixed Glass panel, then I expect, services of a professional glass installer may be needed - at a much higher cost. Good luck! Roof Opening Panel Glass — Rear Fixed - Removal and Installation - 2009 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Roof Opening Panel — Exploded View Illustrations - 2009 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf
-

2011 Ford Edge Rear Suspension Torque Specs Needed
Haz replied to mdk1016's topic in Brakes, Chassis & Suspension
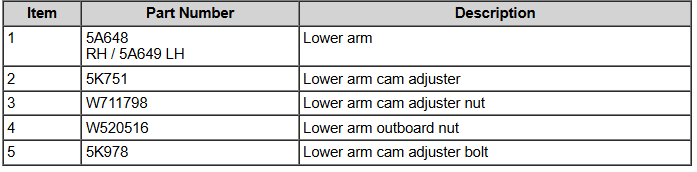
Lower Arm illustration and guidance from the Workshop Manual... NOTICE: Suspension fasteners affect performance of vital components and systems and their failure may result in major service expense. If replacement is necessary install new parts with the same part numbers or equivalent part. Do not use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Tighten the fasteners to specification during reassembly. NOTICE: Tighten the suspension bushing fasteners with the weight of the vehicle resting on the wheels and tires or incorrect clamp load and bushing damage may occur. Good luck! -

2011 Ford Edge Rear Suspension Torque Specs Needed
Haz replied to mdk1016's topic in Brakes, Chassis & Suspension
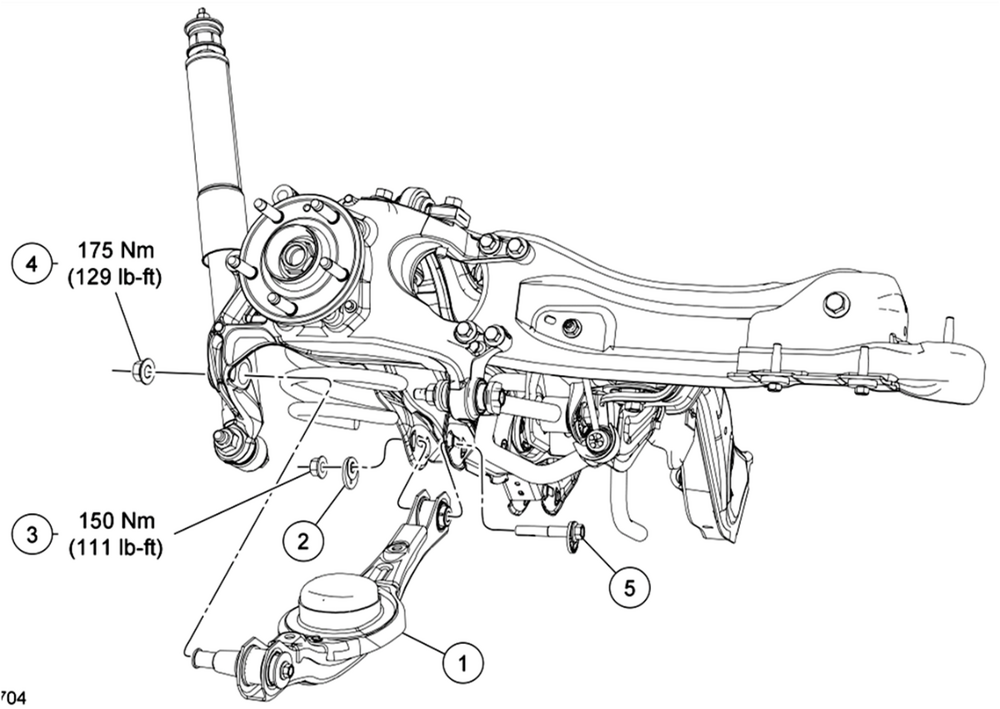
Welcome to the Forum @mdk1016! From the 2011 Edge Workshop Manual... Rear Suspension Torque Specifications Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Lower arm cam adjuster nut 150 111 — Lower arm outboard nut 175 129 — Parking brake cable bolt 18 — 159 Shock absorber lower nut 225 166 — Shock absorber upper nut 25 18 — Stabilizer bar bracket nut 55 41 — Stabilizer bar link upper and lower nut 40 30 — Toe link inboard nut 200 148 — Toe link outboard nut 175 129 — Upper arm inboard nut 175 129 — Upper arm outboard bolts 175 129 — Wheel hub and bearing bolt 115 85 — Wheel hub nuta — — — Trailing arm bracket-to-frame bolts 48 35 — Trailing arm nut 150 111 — Wheel knuckle-to-trailing arm nuts 103 76 — Wheel speed sensor bolt 7 — 62 Rear Drive Axle/Differential Torque Specifications Description Nm lb-ft Differential housing cover bolts 23 17 Differential housing-to-front insulator bracket bolts 90 66 Filler plug 29 21 Front insulator bracket-to-subframe bolts 90 66 Pinion flange nut 244 180 Rear driveshaft U-joint flange bolts 70 52 Side insulator bracket-to-rear axle differential bolts 90 66 AWD vehicles NOTICE: Do not tighten the rear wheel hub nut with the vehicle on the ground. Tighten the wheel hub nut to specification before the vehicle is lowered to the ground. Wheel bearing damage occurs if the wheel bearing is loaded with the weight of the vehicle applied. NOTE: Apply the brake to keep the halfshaft from rotating. Position the halfshaft in the wheel hub and bearing assembly and use the previously removed wheel hub nut to seat the halfshaft. Tighten to 350 Nm (258 lb-ft). Remove and discard the wheel hub nut. NOTICE: Install and tighten the new wheel hub nut to specification within 5 minutes of starting it on the threads. Always install a new wheel hub nut after loosening, or when not tightening within the specified time, or damage to the components may occur. Install a new wheel hub nut. Tighten to 350 Nm (258 lb-ft). Good luck! -
TECHNICAL SERVICE BULLETIN Misfire With DTC(s) P0301, P0302, P0303, And/Or P0304 Stored In The PCM 25-2074 06 March 2025 This bulletin supersedes 24-2384. Reason for update: vehicle models affected Model: Ford 2025 Bronco Engine: 2.3L EcoBoost 2023-2025 Escape Engine: 1.5L EcoBoost Engine: 2.0L EcoBoost 2025 Explorer Engine: 2.3L EcoBoost 2024-2025 Mustang Engine: 2.3L EcoBoost 2025 Ranger Engine: 2.3L EcoBoost Lincoln 2023-2025 Corsair Engine: 2.0L EcoBoost 2024-2025 Nautilus Engine: 2.0L EcoBoost Engine: 2.0L EcoBoost Hybrid Markets: North American markets only Issue: Some of the vehicles listed in the Model statement above may exhibit an engine misfire condition with DTCs P0301, P0302, P0303 and/or P0304 set in the PCM. Action: For vehicles that meet all of the criteria in the Issue and Model statements, follow the Service Procedure to diagnose the vehicle. Warranty Status: Information Only. Repair/Claim Coding Causal Part: IN Condition Code: -1 Service Procedure NOTE: This article is for information only. Determine the causal part number and use available labor times in the SLTS Manual or claim M-time in accordance with the Warranty and Policy Manual, do not use this article number as the M-Time labor operation. Causal part number IN in this article refers to the information only status and is not able to be claimed. 1. Remove and inspect the condition of all spark plugs. Refer to the WSM, Section 303-07. Are any spark plugs damaged? (1). Yes - proceed to Step 2. (2). No - this article does not apply, replacement of the spark plugs is not necessary, proceed with normal diagnostics found in the WSM. 2. Inspect the 12v battery positive and negative terminals for a loose condition, refer to WSM, Section 414-01 and repair as necessary. 3. Inspect all PCM ground circuitry for loose connections and/or high resistance and repair as necessary. 4. Use a borescope to inspect the condition of the affected pistons and cylinder walls. Refer to Figures 1-3 for examples of normal cylinder wall wear and Figures 4-5 for examples of damaged cylinder walls. Additional examples of engine wear can be found in the Engine Failure Analysis GSB > Cylinder Wall and Piston Skirt Inspection. Do the pistons and/or cylinder walls appear to be damaged? Figure 1 - Showing normal cylinder wall wear Figure 2 - Showing normal cylinder wall wear Figure 3 - Showing normal cylinder wall wear Figure 4 - Showing a damaged cylinder wall Figure 5 - Showing a damaged cylinder wall (1). Yes - remove the cylinder head to perform a more detailed inspection of the suspect damage. Refer to the Engine Failure Analysis GSB > Cylinder Wall and Piston Skirt Inspection and repair as necessary. For cylinder head removal, refer to the WSM, Section 303-01. (2). No - perform a compression test and cylinder leakage test following WSM, Section 303-00 and repair as necessary. 5. Replace all damaged spark plugs. Do not discard the damaged spark plugs so Ford can retrieve them following the warranty parts return process. 6. Submit a GCR and include photos of damaged components, images from the borescope analysis and anything else of interest that was found during the repair. These images will help improve engine quality for future model vehicles. (1). Do not use the Report A Problem link to submit the GCR. © 2025 Ford Motor Company All rights reserved. NOTE: The information in Technical Service Bulletins is intended for use by trained, professional technicians with the knowledge, tools, and equipment to do the job properly and safely. It informs these technicians of conditions that may occur on some vehicles, or provides information that could assist in proper vehicle service. The procedures should not be performed by "do-it-yourselfers". Do not assume that a condition described affects your car or truck. Contact a Ford or Lincoln dealership to determine whether the Bulletin applies to your vehicle. Warranty Policy and Extended Service Plan documentation determine Warranty and/or Extended Service Plan coverage unless stated otherwise in the TSB article. The information in this Technical Service Bulletin (TSB) was current at the time of printing. Ford Motor Company reserves the right to supersede this information with updates. The most recent information is available through Ford Motor Company's on-line technical resources. TSB 25-2074 - Misfire With DTCs P0301, P0302, P0303, And-Or P0304 Stored In The PCM - 03-06-2025.pdf
-
It's worth noting that a visit to the dealership is required for correction, and that no impending OTA update is mentioned as an alternative remedy. Thanks, Bunky!
- 1 reply
-
- 2
-

-
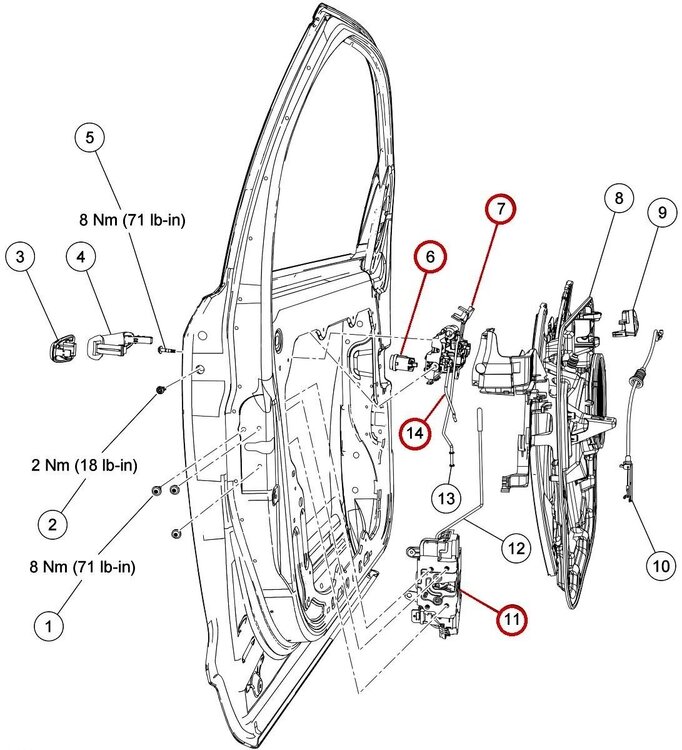
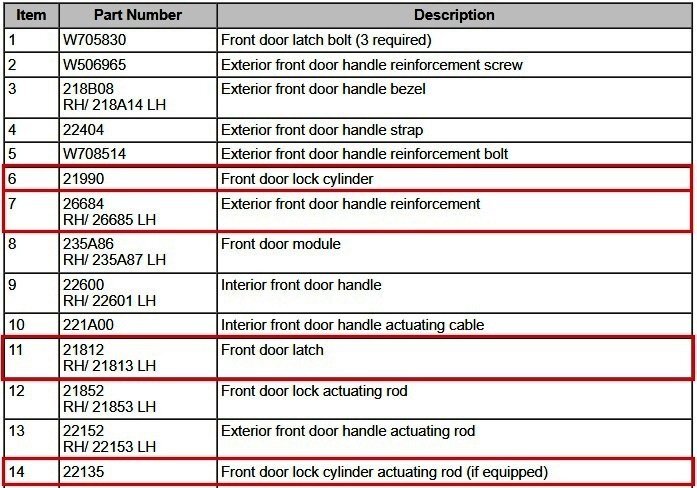
Per the sections of the 2013 Edge Workshop Manual attached below as PDF documents, and the following illustration: The door lock cylinder (item 6), mounts into the door handle reinforcement (item 7), and a D-slot in the back of the door lock cylinder engages with the D-shaped end of the door lock cylinder actuating rod (item 14), which translates the door lock cylinder rotation into a lock/unlock effect in the door latch (item 11)... Only the door lock cylinder (item 6) is removable from the door's exterior, allowing inspection of the door lock cylinder's D-slot rotation, and, the position & condition of the D-shaped end of the door lock actuating rod (item 14). If these items appear good, then removing the interior door panel will be necessary to assess the other components. The following YouTube video provides a beginning-to-end glimpse of what may be involved in that subsequent inspection... Good luck! Exterior Door Handle - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Door Lock Cylinder - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Front Door Handles, Locks and Latches — Exploded View - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Front Door Latch - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Door Handle Reinforcement - Removal and Installation - 2013 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf
-
@Bunky: Thanks for the heads-up and I apologize for the confusion! I've circled back, and I do not find this Special Service Message cross-referenced as applying to 2021-2025 Edge/Nautilus. My further cross-checking indicates SSM 53350 applies to F-150, Maverick, Mustang, Mustang Mach-E, and Transit. Why they didn't spell-out this short of an affected-models listing, I'll never know. I will cross-reference future "Various Vehicles" announcements to avoid similar occurrences. Once again, gratitude for the heads-up!
-
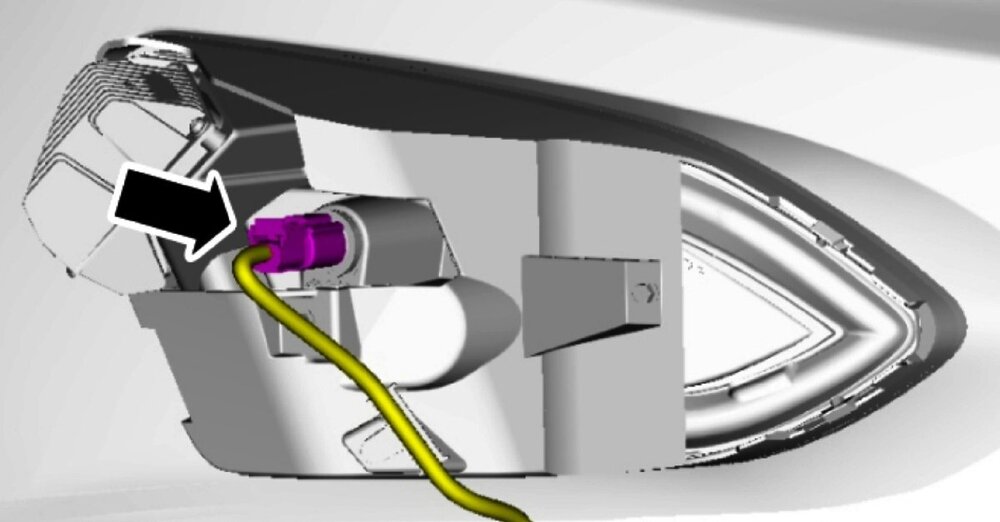
The Workshop Manual provides an aiming procedure for headlamps, but offers no aiming procedure for fog lamps. The following Workshop Manual illustration of the fog lamp housing depicts the fog lamp bulb's location, but it's not absolutely clear if this directly coincides with the location of feature you've highlighted above... If it is the same location, then the presumed hex-socketed adjustment screw may actually be a removable plug intended to prevent debris from entering the fog lamp housing prior to installation of the fog lamp bulb. Closer detail of the above-illustrated fog lamp electrical connector is shown in this photo... Workshop Manual procedures relating to removal and installation of the front bumper cover and the fog lamp assembly are attached below as PDF documents... Good luck! Front Fog Lamp - Removal and Installation - 2024 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf Front Bumper Cover - Removal and Installation - 2024 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf
-
My further cross-checking indicates SSM 53530 applies to F-150, Maverick, Mustang, Mustang Mach-E, and Transit. SSM 53530 - 2021-2025 Various Vehicles - Heated/Cooled Seats, Heated Steering Wheel And/Or Front/Rear Defrost Inoperative After Remote Start Event Some 2021-2025 Ford vehicles may exhibit a condition where heated/cooled seats, heated steering wheel and/or front/rear defrost features will not turn on after a remote start is performed through the FordPass application or the key fob. These features then operate normally when commanded in the center display screen. This may be due to the customer not setting up their "Climate Settings" through the FordPass mobile application. To correct this condition, inform the customer they should perform a remote start from FordPass and then adjust the "Climate Settings" in the FordPass application as desired. These settings only need to be set once and will persist through subsequent remote starts. Heated and cooled seats will be set to Level 2 when turned ON via "Climate Settings" in FordPass during a remote start event. This is normal operating characteristic. This condition does not affect vehicle durability and no additional diagnosis or service is required for this condition at this time.
-
Welcome @Clint in Kan! Have you had the battery load-tested to ensure it is not failing or in a failed state? Per the Workshop Manual section attached below as a PDF document, while our vehicles employ load shedding strategies to conserve power during reduced battery state-of-charge conditions, a failing or failed battery can cause modules and their related components to behave in unexpected ways. Given that the symptoms you describe materialized in a single day, particularly involving the Instrument Panel Cluster (IPC), you may want to have the battery tested, even if it has been replaced within the last few months. Good luck! Charging System - 2.0L EcoBoost - System Operation and Component Description - 2015 Edge Workshop Manual.pdf
- 11 replies
-
- 2
-

-
- body control module
- bcm
-
(and 1 more)
Tagged with:
-
-
New flags in @Haz's signature?
-

Back when I started working at Ford, the United Auto Workers (UAW) labor union used the Crossed Flags to symbolize UAW members who worked in the Canadian & American operations of the so-called Big Three automakers – General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler.
More recently, it occurred to me that the Crossed Flags are a fitting symbol of the Cross-Border Cooperation between the American company Ford, and the Canadian auto workers at Oakville Assembly, who built the Edge-MKX-Nautilus vehicles that we own and regularly discuss here on the Forum.
So, I added the Crossed Flags to my Forum signature.
Flag etiquette dictates that nationality determines which flag appears on the right-hand side of the image…
Canadian version:

American version:

Good luck!
-
-
 1
1
-
- Report
-